|
|
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| − | ==Summary Explanation of Table Listings== | + | ==Status of Basel Convention and Basel Ban by Country== |
| | | | |
| − | ===Basel Convention=== | + | {| class="wikitable sortable" border="0" style="background-color:#ffffff; width:80%;" |
| − | (''See [[Basel Convention]]'')
| + | | style="width:50%"| |
| − | | + | [[File:Basel_Convention_Countries_Map.jpg|300px|Map created using worldmapmaker.com]]<br/> |
| − | ”The Basel Convention on the Transboundary Movement of Hazardous Wastes and their Disposal” was adopted on 21 March 1989 and went into force on 5 May 1992. It establishes a framework of control over the transboundary movements of hazardous wastes.
| + | '''Legend:'''<br/> |
| − | | + | '''<span style="color:#800000">Maroon:</span>''' Basel Convention has entered into force<br/> |
| − | If a country has joined the treaty through the deposit of ratification (r), accession (a), acceptance (A) or Approval (AA) they are considered Parties as of the indicated date of deposit. The total number of such Parties is listed. If a country has signed the treaty but has not yet ratified it, this is indicated by the word “signature”.
| + | '''<span style="color:#808080">Gray:</span>''' Basel Convention has not entered into force/Country is not a party to the Basel Convention<br/> |
| − | | |
| − | ===Organization of Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)===
| |
| − | When the Parties to the Convention sought to make an economic distinction between developed and developing countries in Decision II/12, they chose the divider line established by the OECD — a group which currently has 34 members and and for the most part represent the more highly developed and industrialized countries. This group by far produces the most hazardous waste (estimated at 90%) and by far has the most resources to ensure that it is dealt with responsibly at home. Thus the Basel Ban Decision and Amendment were meant to apply only to these countries. In 1995, the Parties created Annex VII and included the EU countries as well as Liechtenstein (an EFTA member country).
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===European Union===
| |
| − | The Basel Convention allows political or economic integration organizations to join the Convention as Parties to it. The European Commission of the European Economic Community, now known as the European Union, has ratified the Convention as have most of their member states. When it comes time to vote in the Convention, ordinarily the European Commission has the competence to vote the 27 votes of the member states plus one vote for the Commission as a bloc of 28. While the competence over ratification of the treaty itself or its amendments remains the subject of some controversy, it is generally accepted that the European Commission possesses the competence for ratification or accession especially over treaties related to trade. With respect to the Basel Ban Amendment which the Commission has ratified while individual member states have not all taken the somewhat redundant step of likewise ratifying, our table records the Commission and all of the EU countries which (in total 28), while not all having deposited individual ratifications, nevertheless are bound by the Basel Ban as having “Implemented!” it in national law as required by the Waste Shipment Regulation of the European Union.
| |
| | | | |
| − | ===European Economic Agreement===
| |
| − | Additionally the countries of Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway, all members of the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) are also bound by the implementation legislation 259/93 and amendments (see below) due to their obligations under the trade linking agreement between EFTA and the EU known as the European Economic Agreement (EEA). As Norway has ratified the Basel Ban Amendment outright, it is listed as a ratifier of the Basel Ban Amendment while Iceland and Liechtenstein are listed as having implemented it.
| |
| | | | |
| − | ===Basel Ban===
| + | |[[File:Basel_Ban_Amendment_Countries_Map.jpg|300px|Map created using worldmapmaker.com]]<br/> |
| − | ''(See [[Ban Amendment]])''
| |
| − | | |
| − | [[Decision II/12|'''Decision II/12:''']] This decision was passed by a consensus of the 66 Parties at the Second Conference of Parties of the Basel Convention on 25 March 1994. All exports of hazardous wastes from OECD to non-OECD countries would be banned. The ban takes place immediately for final disposal, and for those wastes bound for recycling destinations, the ban would take effect on 31 December 1997.
| |
| − | | |
| − | An X on the table indicates the country joined in the consensus decision.
| |
| − | | |
| − | [[Decision III/1|'''Decision III/1 and Annex VII:''']] This decision was passed by a consensus of the Parties present at the Third Conference of Parties of the Basel Convention on 22 September 1995. It has been determined that there were 87 Parties at that time. The decision established an amendment to the Convention to establish a new Article 4A and an Annex VII. The article obligates Parties that are listed on Annex VII (country members of the OECD, EU and Liechtenstein) to ban exports of hazardous wastes to all countries not listed on Annex VII. The ban would take place immediately for final disposal, and for those wastes bound for recycling destinations, the ban would take effect on 31 December 1997. The Amendment will go into force when 66 countries (3/4ths of the 87 Parties at that time) have ratified it.
| |
| − | | |
| − | An X on the table, indicates the country joined in the consensus decision in 1995. The word “Ratified” and the country flag indicates that the country has deposited its ratification. The word “Implemented” indicates that the country has not ratified but has in fact implemented the agreement in its national policies or laws. However for a full count of ratifications visit the Deposit Box.
| |
| − | | |
| − | [[File:Basel_Convention_Countries_Map.jpg|300px|caption]]<br/> | |
| | '''Legend:'''<br/> | | '''Legend:'''<br/> |
| − | '''Maroon:''' Basel Convention has entered into force<br/> | + | '''<span style="color:red">Red:</span>''' Needed for entry into force - Not ratified<br/> |
| − | '''Gray:''' Basel Convention has not entered into force/Country is not a party to the Basel Convention<br/> | + | '''<span style="color:green">Green:</span>''' Needed for entry into force of Basel Ban - Ratified<br/> |
| − | © worldmapmaker.com | Travel Insurance
| + | '''<span style="color:blue">Blue:</span>''' Not needed for entry into force - Ratified<br/> |
| | + | |} |
| | | | |
| − | [[File:Basel_Ban_Amendment_Countries_Map.jpg|300px|caption]]<br/>
| |
| − | '''Legend:'''<br/>
| |
| − | '''Red:''' Needed for entry into force - Not ratified<br/>
| |
| − | '''Green:''' Needed for entry into force of Basel Ban - Ratified<br/>
| |
| − | '''Blue:''' Not needed for entry into force - Ratified<br/>
| |
| − | © worldmapmaker.com | Travel Insurance
| |
| | | | |
| − | [[File:Basel_Convention_Countries_Map.jpg|300px|thumb|'''Legend:'''<br/>
| |
| − | '''Maroon:''' Basel Convention has entered into force<br/>
| |
| − | '''Gray:''' Basel Convention has not entered into force/Country is not a party to the Basel Convention<br/>
| |
| − | © worldmapmaker.com - Travel Insurance]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[File:Basel_Ban_Amendment_Countries_Map.jpg|300px|thumb|'''Legend:'''<br/>
| |
| − | '''Red:''' Needed for entry into force - Not ratified<br/>
| |
| − | '''Green:''' Needed for entry into force of Basel Ban - Ratified<br/>
| |
| − | '''Blue:''' Not needed for entry into force - Ratified<br/>
| |
| − | © worldmapmaker.com - Travel Insurance]]
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==Basel Convention and Basel Ban Country Status Table==
| |
| | | | |
| | {| class="wikitable sortable" border="1" style="text-align: center;" | | {| class="wikitable sortable" border="1" style="text-align: center;" |
| Line 1,216: |
Line 1,180: |
| | | | |
| | '''''General Note:''''' ''Due to the constant change in status of various treaties, amendments and protocols, the Basel Action Network cannot ensure the absolute accuracy of all of these listings in this table. We therefore appreciate those that will call our attention to any errors or changes in status to assist us in updating the table as accurately and in as timely a manner as possible.'' | | '''''General Note:''''' ''Due to the constant change in status of various treaties, amendments and protocols, the Basel Action Network cannot ensure the absolute accuracy of all of these listings in this table. We therefore appreciate those that will call our attention to any errors or changes in status to assist us in updating the table as accurately and in as timely a manner as possible.'' |
| | + | |
| | + | |
| | + | ==Summary Explanation of Table Listings== |
| | + | |
| | + | ===Basel Convention=== |
| | + | (''See [[Basel Convention]]'') |
| | + | |
| | + | ”The Basel Convention on the Transboundary Movement of Hazardous Wastes and their Disposal” was adopted on 21 March 1989 and went into force on 5 May 1992. It establishes a framework of control over the transboundary movements of hazardous wastes. |
| | + | |
| | + | If a country has joined the treaty through the deposit of ratification (r), accession (a), acceptance (A) or Approval (AA) they are considered Parties as of the indicated date of deposit. The total number of such Parties is listed. If a country has signed the treaty but has not yet ratified it, this is indicated by the word “signature”. |
| | + | |
| | + | ===Organization of Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)=== |
| | + | When the Parties to the Convention sought to make an economic distinction between developed and developing countries in Decision II/12, they chose the divider line established by the OECD — a group which currently has 34 members and and for the most part represent the more highly developed and industrialized countries. This group by far produces the most hazardous waste (estimated at 90%) and by far has the most resources to ensure that it is dealt with responsibly at home. Thus the Basel Ban Decision and Amendment were meant to apply only to these countries. In 1995, the Parties created Annex VII and included the EU countries as well as Liechtenstein (an EFTA member country). |
| | + | |
| | + | ===European Union=== |
| | + | The Basel Convention allows political or economic integration organizations to join the Convention as Parties to it. The European Commission of the European Economic Community, now known as the European Union, has ratified the Convention as have most of their member states. When it comes time to vote in the Convention, ordinarily the European Commission has the competence to vote the 27 votes of the member states plus one vote for the Commission as a bloc of 28. While the competence over ratification of the treaty itself or its amendments remains the subject of some controversy, it is generally accepted that the European Commission possesses the competence for ratification or accession especially over treaties related to trade. With respect to the Basel Ban Amendment which the Commission has ratified while individual member states have not all taken the somewhat redundant step of likewise ratifying, our table records the Commission and all of the EU countries which (in total 28), while not all having deposited individual ratifications, nevertheless are bound by the Basel Ban as having “Implemented!” it in national law as required by the Waste Shipment Regulation of the European Union. |
| | + | |
| | + | ===European Economic Agreement=== |
| | + | Additionally the countries of Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway, all members of the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) are also bound by the implementation legislation 259/93 and amendments (see below) due to their obligations under the trade linking agreement between EFTA and the EU known as the European Economic Agreement (EEA). As Norway has ratified the Basel Ban Amendment outright, it is listed as a ratifier of the Basel Ban Amendment while Iceland and Liechtenstein are listed as having implemented it. |
| | + | |
| | + | ===Basel Ban=== |
| | + | ''(See [[Ban Amendment]])'' |
| | + | |
| | + | [[Decision II/12|'''Decision II/12:''']] This decision was passed by a consensus of the 66 Parties at the Second Conference of Parties of the Basel Convention on 25 March 1994. All exports of hazardous wastes from OECD to non-OECD countries would be banned. The ban takes place immediately for final disposal, and for those wastes bound for recycling destinations, the ban would take effect on 31 December 1997. |
| | + | |
| | + | An X on the table indicates the country joined in the consensus decision. |
| | + | |
| | + | [[Decision III/1|'''Decision III/1 and Annex VII:''']] This decision was passed by a consensus of the Parties present at the Third Conference of Parties of the Basel Convention on 22 September 1995. It has been determined that there were 87 Parties at that time. The decision established an amendment to the Convention to establish a new Article 4A and an Annex VII. The article obligates Parties that are listed on Annex VII (country members of the OECD, EU and Liechtenstein) to ban exports of hazardous wastes to all countries not listed on Annex VII. The ban would take place immediately for final disposal, and for those wastes bound for recycling destinations, the ban would take effect on 31 December 1997. The Amendment will go into force when 66 countries (3/4ths of the 87 Parties at that time) have ratified it. |
| | + | |
| | + | An X on the table, indicates the country joined in the consensus decision in 1995. The word “Ratified” and the country flag indicates that the country has deposited its ratification. The word “Implemented” indicates that the country has not ratified but has in fact implemented the agreement in its national policies or laws. However for a full count of ratifications visit the Deposit Box. |
Status of Basel Convention and Basel Ban by Country
|
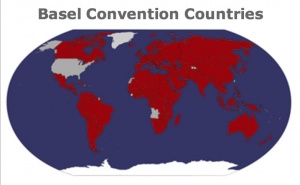
Legend:
Maroon: Basel Convention has entered into force
Gray: Basel Convention has not entered into force/Country is not a party to the Basel Convention
|
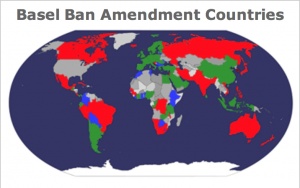
Legend:
Red: Needed for entry into force - Not ratified
Green: Needed for entry into force of Basel Ban - Ratified
Blue: Not needed for entry into force - Ratified
|
| Country (Annex VII shaded)
|
Basel Party
|
Ban Decision II/12
|
Ban Decision III/1
|
| Afghanistan
|
25 March 2013
|
|
|
| Albania
|
29 Jun 1999 (a)
|
|

Ratified!
27 Oct 2005 (A)
|
| Algeria
|
15 Sep 1998 (a)
|
|
|
| Andorra
|
23 Jul 1999 (a)
|
|
Ratified!
23 Jul 1999 (A)
|
| Angola
|
|
|
|
| Antigua and Barbuda
|
05 Apr 1993 (a)
|
X
|
X
|
| Argentina
|
27 Jun 1991 (r)
|
X
|

Ratified!
19 Sept 2011
|
| Armenia
|
01 Oct 1999 (a)
|
|
|
| Australia
|
05 Feb 1992 (a)
|
X
|
X
|
| Austria
|
12 Jan 1993 (r)
|
X
|

Ratified!
17 Oct 1999 (A)
|
| Azerbaijan
|
01 Jun 2001 (a)
|
|
|
| Bahamas
|
12 Aug 1992 (a)
|
X
|
X
|
| Bahrain
|
15 Oct 1992 (r)
|
|

Ratified!
25 Jul 2005
|
| Bangladesh
|
01 Apr 1993 (a)
|
X
|
X
|
| Barbados
|
24 Aug 1995 (a)
|
|
|
| Belarus
|
10 Dec 1999 (a)
|
|
|
| Belgium
|
01 Nov 1993 (r)
|
X
|

Ratified!
20 Jun 2003
|
| Belize
|
23 May 1997 (a)
|
|
|
| Benin
|
04 Dec 1997 (a)
|
|
Ratified!
22 Jan 2014
|
| Bhutan
|
26 Aug 2002 (a)
|
|
|
| Bolivia (Plurinational State of)
|
15 Nov 1996 (r)
|
|

Ratified!
31 Mar 2005
|
| Bosnia and Herzegovina
|
16 Mar 2001 (a)
|
|
|
| Botswana
|
20 May 1998 (a)
|
|
Ratified!
17 Jun 2004 (A)
|
| Brazil
|
01 Oct 1992 (a)
|
X
|
X
|
| Brunei Darussalam
|
16 Dec 2002 (a)
|
|

Ratified!
16 Dec 2002 (A)
|
| Bulgaria
|
16 Feb 1996 (a)
|
|
Ratified!
15 Feb 2000
|
| Burkina Faso
|
04 Nov 1999(a)
|
|
|
| Burundi
|
06 Jan 1997 (a)
|
|
|
| Cambodia
|
02 Mar 2001 (a)
|
|
|
| Cameroon
|
02 Sep 2001 (a)
|
|
|
| Canada
|
28 Aug 1992 (r)
|
X
|
X
|
| Cabo Verde
|
02 Jul 1999 (a)
|
|
|
| Central African Republic
|
24 Feb 2006 (a)
|
|
|
| Chad
|
10 Mar 2004 (a)
|
|
|
| Chile
|
11 Aug 1992 (r)
|
X
|

Ratified!
12 Aug 2009 A
|
| China
|
17 Dec 1991 (r)
|
X
|

Ratified!
01 May 2001
|
| Colombia
|
31 Dec 1996 (r)
|
|

Ratified!
10 Jun 2014
|
| Comoros
|
31 Oct 1994 (a)
|
|
|
| Congo, Republic of
|
20 April 2007 (a)
|
|

Ratified!
02 Sept 2014
|
| Congo, Democratic Republic of
|
06 Oct 1994 (a)
|
|
|
| Cook Islands
|
29 Jun 2004 (a)
|
|

Ratified!
29 Jun 2004 (A)
|
| Costa Rica
|
07 Mar 1995 (a)
|
|
X
|
| Cote d'Ivoire
|
01 Dec 1994 (a)
|
|

Ratified!
24 Sept 2013
|
| Croatia
|
09 May 1994 (a)
|
X
|

Implemented!
X
|
| Cuba
|
03 Oct 1994 (a)
|
|
X
|
| Cyprus
|
17 Sep 1992 (r)
|
X
|

Ratified!
07 Jul 2000 (A)
|
| Czech Republic
|
30 Sep 1993 (d)
|
X
|
Ratified!
28 Feb 2000 (A)
|
| Denmark
|
06 Feb 1994 (AA)
|
X
|

Ratified!
10 Sep 1997 (AA)
|
| Djibouti
|
31 May 2002 (a)
|
|
|
| Dominica
|
05 May 1998 (a)
|
|
|
| Dominican Republic
|
10 Jul 2000 (a)
|
|
|
| East Timor
|
|
|
|
| Ecuador
|
23 Feb 1993 (r)
|
X
|

Ratified!
06 Mar 1998
|
| Egypt
|
08 Jan 1993 (a)
|
X
|

Ratified!
27 Jan 2004
|
| El Salvador
|
13 Dec 1991 (r)
|
X
|
X
|
| Equatorial Guinea
|
07 Feb 2003 (a)
|
|
|
| Eritrea
|
10 Mar 2005 (a)
|
|
|
| Estonia
|
21Jul 1992 (a)
|
X
|

Ratified!
02 Aug 2001
|
| Ethiopia
|
12 Apr 2000 (a)
|
|

Ratified!
08 Oct 2003
|
| European Union*
|
07 Feb 1994 (AA)
|
X
|

Ratified!
30 Sep 1997 (AA)
|
| Fiji
|
|
|
|
| Finland
|
19 Nov 1991 (A)
|
X
|

Ratified!
05 Jun 1996 (A)
|
| France
|
07 Jan 1991 (AA)
|
X
|
Ratified!
18 Nov 2003 (AA)
|
| Gabon
|
6 Jun 2008 (a)
|
|
|
| Gambia
|
15 Dec 1997 (a)
|
|

Ratified!
09 Mar 2001
|
| Georgia
|
20 May 1999 (a)
|
|
|
| Germany
|
21 Apr 1995 (r)
|
X
|

Ratified!
24 May 2002 (A)
|
| Ghana
|
30 May 2003 (a)
|
|
Ratified!
09 Jun 2005
|
| Greece
|
04 Aug 1994 (r)
|
X
|

Ratified!
12 Jul 2010
|
| Grenada
|
|
|
|
| Guatemala
|
15 May 1995 (r)
|
|

Ratified!
26 Dec 2013
|
| Guinea
|
26 Apr 1995 (r)
|
|
X
|
| Guinea-Bissau
|
09 Feb 2005 (a)
|
|
|
| Guyana
|
04 Apr 2001 (a)
|
|
|
| Haiti
|
signature
|
|
|
| Honduras
|
27 Dec 1995 (a)
|
|
|
| Hungary
|
21 May 1990 (AA)
|
X
|

Ratified!
25 May 2004 (AA)
|
| Iceland
|
28 Jun 1995 (a)
|
|
Implemented!
|
| India
|
24 Jun 1992 (r)
|
X
|
X
|
| Indonesia
|
20 Sep 1993 (a)
|
X
|

Ratified!
24 Oct 2005
|
| Iran, Islamic Republic of
|
05 Jan 1993 (a)
|
X
|
X
|
| Iraq
|
02 May 2011 (a)
|
|
|
| Ireland
|
07 Feb 1994 (r)
|
X
|

Ratified!
13 Nov 2009
|
| Israel
|
04 Dec 1994 (r)
|
|

Implemented!
X
|
| Italy
|
07 Feb 1994 (r)
|
X
|

Ratified!
3 March 2009
|
| Jamaica
|
23 Jan 2003 (a)
|
|
|
| Japan
|
17 Sep 1993 (a)
|
X
|
X
|
| Jordan
|
22 Jun 1989 (AA)
|
X
|

Ratified!
06 Dec 2004 (AA)
|
| Kazakhstan
|
03 Jun 2003 (a)
|
|
|
| Kenya
|
01 Jun 2000 (a)
|
|

Ratified!
9 Sep 2009 A
|
| Kiribati
|
07 Sep 2000 (a)
|
|
|
| Korea, Democratic People's Republic of
|
10 Jul 2008 (a)
|
|
|
| Korea, Republic of
|
28 Feb 1994 (a)
|
|
X
|
| Kuwait
|
11 Oct 1993 (r)
|
X
|

Ratified!
12 May 2006
|
| Kyrgyzstan
|
13 Aug 1996 (a)
|
|
|
| Lao, People's Democratic Republic
|
21 September 2010 (a)
|
|
|
| Latvia
|
14 Apr 1992 (a)
|
X
|

Ratified!
18 Dec 2003 (A)
|
| Lebanon
|
21 Dec 1994 (r)
|
|
X
|
| Lesotho
|
31 May 2000 (a)
|
|

Ratified!
22 Feb 2012 A
|
| Liberia
|
22 Sep 2004 (a)
|
|
Ratified!
16 Sep 2005 (A)
|
| Libya
|
12 Jul 2001 (a)
|
|
|
| Liechtenstein
|
27 Jan 1992 (r)
|
X
|

Ratified!
20 May 2003 (A)
|
| Lithuania
|
24 Apr 1999 (a)
|
|

Ratified!
7 Nov 2003 (A)
|
| Luxembourg
|
07 Feb 1994 (r)
|
X
|

Ratified!
14 Aug 1997
|
| Madagascar
|
02 Jun 1999 (a)
|
|
|
| Malawi
|
21 Apr 1994 (a)
|
X
|
X
|
| Malaysia
|
08 Oct 1993 (a)
|
X
|

Ratified!
26 Oct 2001
|
| Maldives
|
28 Apr 1992 (a)
|
X
|
X
|
| Mali
|
12 May 2000 (a)
|
|
|
| Malta
|
19 Jun 2000 (a)
|
|

Implemented!
|
| Marshall Islands
|
27 Jan 2003 (a)
|
|
|
| Mauritania
|
16 Aug 1996 (a)
|
|
|
| Mauritius
|
24 Nov 1992 (a)
|
X
|

Ratified!
09 Nov 2004
|
| Mexico
|
22 Feb 1991 (r)
|
X
|

Implemented!
X
|
| Micronesia, Federated States of
|
06 Sep 1995 (a)
|
|
|
| Moldova, Republic of
|
02 Jul 1998 (a)
|
|

Ratified!
18 Nov 2008 (A)
|
| Monaco
|
31 Aug 1992 (a)
|
X
|

Ratified!
20 March 2013 AA
|
| Mongolia
|
15 Apr 1997 (a)
|
|
|
| Montenegro
|
23 Oct 2006 (d)
|
|

Ratified!
23 Oct 2006 (d)
|
| Morocco
|
28 Dec 1995 (a)
|
|

Ratified!
10 Sep 2004 (AA)
|
| Mozambique
|
13 Mar 1997 (a)
|
|
|
| Myanmar
|
06 January 2015 (A)
|
|
|
| Namibia
|
15 May 1995 (a)
|
|
X
|
| Nauru
|
12 Nov 2001 (a)
|
|
|
| Nepal
|
15 Oct 1996 (a)
|
|
|
| Netherlands
|
16 Apr 1993 (A)
|
X
|

Ratified!
22 Jan 2001 (A)
|
| New Zealand
|
20 Dec 1994 (r)
|
|
X
|
| Nicaragua
|
03 Jun 1997 (a)
|
|
|
| Niger
|
17 Jun 1998 (a)
|
|
|
| Nigeria
|
13 Mar 1991 (r)
|
X
|

Ratified!
24 May 2004
|
| Niue
|
|
|
|
| Norway
|
02 Jul 1990 (r)
|
X
|
Ratified!
16 Jul 1997 (A)
|
| Oman
|
08 Feb 1995 (a)
|
|

Ratified!
17 May 2004
|
| Pakistan
|
26 Jul 1994 (a)
|
X
|
X
|
| Palau
|
08 September 2011 (a)
|
|
|
| Panama
|
22 Feb 1991 (r)
|
|
Ratified!
07 Oct 1998
|
| Papua New Guinea
|
01 Sep 1995 (a)
|
|
|
| Paraguay
|
28 Sep 1995 (a)
|
|

Ratified!
28 Aug 1998
|
| Peru
|
23 Nov 1993 (a)
|
X
|

Ratified!
30 Mar 2015 (A)
|
| Philippines
|
21 Oct 1993 (r)
|
X
|
X
|
| Poland
|
20 Mar 1992 (r)
|
X
|

Ratified!
29 Jan 2003 (A)
|
| Portugal
|
26 Jan 1994 (r)
|
X
|
Ratified!
30 Oct 2000
|
| Qatar
|
09 Aug 1995 (a)
|
|
Ratified!
28 Feb 2002
|
| Romania
|
27 Feb 1991 (a)
|
X
|

Ratified!
17 Jul 2002 (A)
|
| Russian Federation
|
31 Jan 1995 (r)
|
|
X
|
| Rwanda
|
07 Jan 2004 (a)
|
|
|
| Saint Kitts and Nevis
|
07 Sep 1994 (a)
|
|
|
| Saint Lucia
|
09 Dec 1993 (a)
|
X
|
Ratified!
22 Jan 2002
|
| Saint Vincent and Granadines
|
02 Dec 1996 (a)
|
|
|
| Samoa
|
22 Mar 2002 (a)
|
|
|
| Sao Tome and Principe
|
12 November 2013 (a)
|
|
|
| Saudi Arabia
|
07 Mar 1990 (r)
|
X
|

Ratified!
10 Jan 2013
|
| Senegal
|
10 Nov 1992 (a)
|
X
|
X
|
| Serbia
|
18 April 2000 (a)
|
|

Ratified!
22 Nov 2002 (A)
|
| Seychelles
|
11 May 1993 (a)
|
X
|
X
|
| Sierra Leone
|
|
|
|
| Singapore
|
02 Jan 1996 (a)
|
|
|
| Slovak Republic
|
28 May 1993 (d)
|
X
|

Ratified!
11 Sep 1998 (A)
|
| Slovenia
|
07 Oct 1993 (a)
|
X
|

Ratified!
01 Dec 2004
|
| Solomon Islands
|
|
|
|
| Somalia
|
26 July 2010 (a)
|
|
|
| South Africa
|
05 May 1994 (a)
|
X
|
X
|
| South Sudan
|
|
|
|
| Spain
|
07 Feb 1994 (r)
|
X
|
Ratified!
07 Aug 1997 (A)
|
| Sri Lanka
|
28 Aug 1992 (a)
|
|

Ratified!
29 Jan 1999
|
| State of Palestine
|
02 January 2015 (a)
|
|
|
| Sudan
|
09 Jan 2006 (a)
|
|
|
| Suriname
|
20 September 2011 (a)
|
|
|
| Swaziland
|
08 Aug 2005 (a)
|
|
|
| Sweden
|
02 Aug 1991 (r)
|
X
|

Ratified!
10 Sep 1997 (A)
|
| Switzerland
|
31 Jan 1990 (r)
|
X
|

Ratified!
07 Nov 2002 (A)
|
| Syrian Arab Republic
|
22 Jan 1992 (r)
|
|

Ratified!
05 Oct 2004
|
| Tanzania, United Republic of
|
07 Apr 1993 (a)
|
X
|

Ratified!
26 Aug 2002
|
| Tajikistan
|
|
|
|
| Thailand
|
24 Nov 1997 (r)
|
|
|
| The former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia
|
16 Feb 1997 (a)
|
|

Ratified!
18 Nov 2004
|
| Togo
|
02 Jul 2004 (a)
|
|
|
| Tonga
|
26 March 2010 (a)
|
|
|
| Trinidad and Tobago
|
18 Feb 1994 (a)
|
X
|

Ratified!
12 Jan 2000
|
| Tunisia
|
11 Oct 1995 (a)
|
|

Ratified!
26 Mar 1999
|
| Turkey
|
22 Jun 1994 (r)
|
X
|

Ratified!
27 Aug 2003
|
| Turkmenistan
|
25 Sep 1996 (a)
|
|
|
| Tuvalu
|
|
|
|
| Uganda
|
11 Mar 1999 (a)
|
|
|
| Ukraine
|
08 Oct 1999 (a)
|
|
|
| United Arab Emirates
|
17 Nov 1992 (r)
|
X
|
|
| United Kingdom
|
07 Feb 1994 (r)
|
X
|

Ratified!
13 Oct 1997
|
| United States
|
signature
|
|
X
|
| Uruguay
|
22 Dec 1991 (r)
|
X
|

Ratified!
10 Mar 1999
|
| Uzbekistan
|
07 Feb 1996 (a)
|
|
|
| Vanuatu
|
|
|
|
| Venezuela
|
03 Mar 1998 (r)
|
|
|
| Viet Nam
|
13 Mar 1995 (a)
|
|
X
|
| Yemen, Republic of
|
21 Feb 1996 (a)
|
|
|
| Zambia
|
15 Nov 1994 (a)
|
|
Ratified!
27 Jul 2011
|
| Zimbabwe
|
01 March 2012 (a)
|
|
|
| TOTALS:
|
183 Parties
|
|
81 Ratified
(4 More Implemented)
|
* Gray shading indicates an Annex VII country.
General Note: Due to the constant change in status of various treaties, amendments and protocols, the Basel Action Network cannot ensure the absolute accuracy of all of these listings in this table. We therefore appreciate those that will call our attention to any errors or changes in status to assist us in updating the table as accurately and in as timely a manner as possible.
Summary Explanation of Table Listings
Basel Convention
(See Basel Convention)
”The Basel Convention on the Transboundary Movement of Hazardous Wastes and their Disposal” was adopted on 21 March 1989 and went into force on 5 May 1992. It establishes a framework of control over the transboundary movements of hazardous wastes.
If a country has joined the treaty through the deposit of ratification (r), accession (a), acceptance (A) or Approval (AA) they are considered Parties as of the indicated date of deposit. The total number of such Parties is listed. If a country has signed the treaty but has not yet ratified it, this is indicated by the word “signature”.
Organization of Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)
When the Parties to the Convention sought to make an economic distinction between developed and developing countries in Decision II/12, they chose the divider line established by the OECD — a group which currently has 34 members and and for the most part represent the more highly developed and industrialized countries. This group by far produces the most hazardous waste (estimated at 90%) and by far has the most resources to ensure that it is dealt with responsibly at home. Thus the Basel Ban Decision and Amendment were meant to apply only to these countries. In 1995, the Parties created Annex VII and included the EU countries as well as Liechtenstein (an EFTA member country).
European Union
The Basel Convention allows political or economic integration organizations to join the Convention as Parties to it. The European Commission of the European Economic Community, now known as the European Union, has ratified the Convention as have most of their member states. When it comes time to vote in the Convention, ordinarily the European Commission has the competence to vote the 27 votes of the member states plus one vote for the Commission as a bloc of 28. While the competence over ratification of the treaty itself or its amendments remains the subject of some controversy, it is generally accepted that the European Commission possesses the competence for ratification or accession especially over treaties related to trade. With respect to the Basel Ban Amendment which the Commission has ratified while individual member states have not all taken the somewhat redundant step of likewise ratifying, our table records the Commission and all of the EU countries which (in total 28), while not all having deposited individual ratifications, nevertheless are bound by the Basel Ban as having “Implemented!” it in national law as required by the Waste Shipment Regulation of the European Union.
European Economic Agreement
Additionally the countries of Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway, all members of the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) are also bound by the implementation legislation 259/93 and amendments (see below) due to their obligations under the trade linking agreement between EFTA and the EU known as the European Economic Agreement (EEA). As Norway has ratified the Basel Ban Amendment outright, it is listed as a ratifier of the Basel Ban Amendment while Iceland and Liechtenstein are listed as having implemented it.
Basel Ban
(See Ban Amendment)
Decision II/12: This decision was passed by a consensus of the 66 Parties at the Second Conference of Parties of the Basel Convention on 25 March 1994. All exports of hazardous wastes from OECD to non-OECD countries would be banned. The ban takes place immediately for final disposal, and for those wastes bound for recycling destinations, the ban would take effect on 31 December 1997.
An X on the table indicates the country joined in the consensus decision.
Decision III/1 and Annex VII: This decision was passed by a consensus of the Parties present at the Third Conference of Parties of the Basel Convention on 22 September 1995. It has been determined that there were 87 Parties at that time. The decision established an amendment to the Convention to establish a new Article 4A and an Annex VII. The article obligates Parties that are listed on Annex VII (country members of the OECD, EU and Liechtenstein) to ban exports of hazardous wastes to all countries not listed on Annex VII. The ban would take place immediately for final disposal, and for those wastes bound for recycling destinations, the ban would take effect on 31 December 1997. The Amendment will go into force when 66 countries (3/4ths of the 87 Parties at that time) have ratified it.
An X on the table, indicates the country joined in the consensus decision in 1995. The word “Ratified” and the country flag indicates that the country has deposited its ratification. The word “Implemented” indicates that the country has not ratified but has in fact implemented the agreement in its national policies or laws. However for a full count of ratifications visit the Deposit Box.






















































































